
By Anne Goodchild and Barbara Ivanov, University of Washington
Two converging trends – the rise of e-commerce and urban population growth – are creating big challenges for cities. Online shoppers are learning to expect the urban freight delivery system to bring them whatever they want, wherever they want it, within one to two hours. That’s especially true during the holidays, as shipping companies hustle to deliver gift orders on time.
City managers and policymakers were already grappling with high demand and competing uses for scarce road, curb and sidewalk space. If cities do not act quickly to revamp the way they manage increasing numbers of commercial vehicles unloading goods in streets and alleys and into buildings, they will drown in a sea of double-parked trucks.
The Supply Chain Transportation and Logistics (SCTL) Center at the University of Washington has formed a new Urban Freight Lab to solve delivery system problems that cities and the business sector cannot handle on their own. Funders of this long-term strategic research partnership include the City of Seattle Department of Transportation (SDOT) and five founding corporate members: Costco, FedEx, Nordstrom, UPS and the U.S. Postal Service.
The core problem facing cities is that they are trying to manage their part of a sophisticated data-powered 21st-century delivery system with tools designed for the 1800s – and they are often trying to do it alone. Consumers can order groceries, clothes and electronics with a click, but most cities only have a stripe of colored paint to manage truck parking at the curb. The Urban Freight Lab brings building managers, retailers, logistics and tech firms, and city government together to do applied research and develop advanced solutions.

Moving more goods, more quickly
We have reached the point where millions of people who live and work in cities purchase more than half of their goods online. This trend is putting tremendous pressure on local governments to rethink how they manage street curb parking and alley operations for trucks and other delivery vehicles. It also forces building operators to plan for the influx of online goods. A few years ago, building concierges may have received a few flower bouquets. Now many are sorting and storing groceries and other goods for hundreds of residents every week.
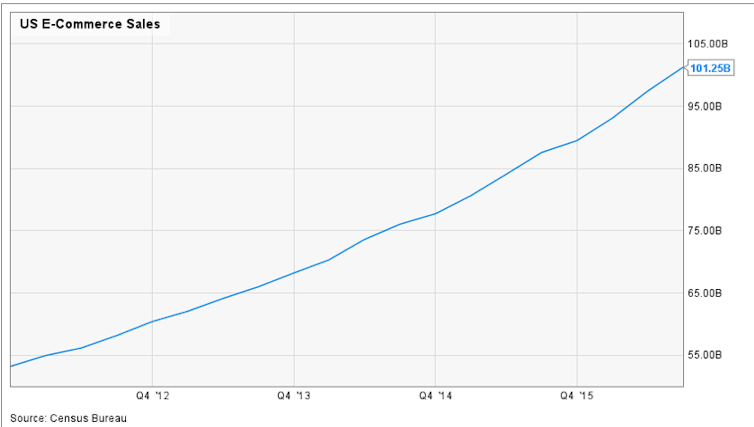
In the first quarter of 2016, almost 8 percent of total U.S. retail sales took place online. Surging growth in U.S. online sales has averaged more than 15 percent year-over-year since 2010. Black Friday web sales soared by 22 percent from 2015 to 2016.
Online shoppers’ expectations for service are also rising. Two out of three shoppers expect to be able to place an order as late as 5:00 p.m. for next-day delivery. Three out of five believe orders placed by noon should be delivered the same day, and one out of four believe orders placed by 4:00 p.m. or later should still be delivered on the same day.
City living and shopping is still all about location, location, location. People are attracted to urban neighborhoods because they prefer to walk more and drive less. Respondents in the 2015 National Multifamily Housing Council-Kingsley Apartment Resident Preferences Survey preferred walking to grocery stores and restaurants rather than driving by seven points. But this lifestyle requires merchants to deliver goods to customers’ homes, office buildings or stores close to where they live.
Smarter delivery systems
SDOT recently published Seattle’s first draft Freight Master Plan, which includes high-level strategies to improve the urban goods delivery system. But before city managers act, they need evidence to prove which concepts will deliver results.
To lay the groundwork for our research, an SCTL team led by Dr. Ed McCormack and graduate students Jose Machado Leon and Gabriela Giron surveyed 523 blocks of Seattle’s downtown (including Belltown, the commercial core, Pioneer Square and International District), South Lake Union and Uptown urban centers in the fall of 2016. They compiled GIS coordinates and infrastructure characteristics for all observable freight loading bays within buildings. Our next step is to combine this information with existing GIS layers of the city’s curbside commercial vehicle load zones and alleys to produce a complete map of Seattle’s urban delivery infrastructure.
In our first research project, the Urban Freight Lab is using data-based process improvement tools to purposefully manage both public and private operations of the Final-50-Feet space. The final 50 feet of the urban delivery system begins when a truck stops at a city-owned curb, commercial vehicle load zone or alley. It extends along sidewalks and through privately owned building freight bays, and may end in common areas within a building, such as the lobby.

One key issue is failed deliveries: Some city residents don’t receive their parcels due to theft or because they weren’t home to accept them. Could there be secure, common drop-off points for multiple carriers to use, attached to bus stops or on the sidewalk?
The most pressing issue is the lack of space for trucks to park and deliver goods downtown. It may be possible to use technology to get more use out of existing commercial vehicle load zones. For example, trucks might be able to use spaces now reserved exclusively for other uses during off-peak hours or seasons.
To analyze the fundamental problems in the urban logistics system, our research team will create process flow maps of each step in the goods delivery process for five buildings in Seattle. We will collect data and build a model to analyze “what if” scenarios for one location. Then we will pilot test several promising low-cost, high-value actions on Seattle streets in the fall of 2017. The pilots may involve actively managing city load zones and alleys to maximize truck use, or changing the way people use freight elevators.

By using information technologies and creative planning, we can make receiving online goods as efficient as ordering them – without clogging our streets or losing our packages.